Fancy a new Factory Worker gig? Read here first before sending your resume off into the job universe. In this write-up, we will provide you with comprehensive advice to create a top-notch Factory Worker resume.
Factory workers are found in industrial settings where they may operate machines, assemble products, maintain or clean equipment or engage in cleaning, checking, and quality control activities. To perform in the job of a Factory worker you need physical stamina and dexterity for sure, but to land the job in the first place you have to present a resume that will attract the attention of hiring managers and recruiters.
If you are a bit clueless on where to even start, fear not. We will explain all the most important aspects of resume writing in our Factory Resume Worker guideline below.
What you can read in this article
Factory Worker Resumes
(Free sample factory worker resume pdf downloads are at the bottom of this page!)
Factory Worker Resume Writing Guide
What should a factory worker put it's resume?
Resume Sections:
1. Contact Information: Name, Address, Cell Phone, Email. Be sure to include alternative contact channels like Facebook Messenger or a landline number if you have one.
2. Career Summary: This is the introduction to your resume consisting of 3-4 sentences explaining your technical competencies, years of experience, and areas of industry focus. If you have post-school credentials mention the most recent ones to finish off your career summary.
3. Qualifications/Certifications Summary: Typically, to secure a job as a Factory Worker, you only require a High School or GED diploma. You may also include formal apprenticeship training certifications professional development that better prepared you to work in a factory environment field like safety training or maintenance workshops. Certain specialized factory worker roles require further training in machine operation or computer programs related to the type of facility you are working in.
4. Relevant Factory Experience: Factory workers are found in a wide range of sectors making any product imaginable, for instance, timber, pulp and paper, food and drink, plastics, textiles, chemicals, and energy. Be specific about your technical tenure and list your employment history by date, company, and job title held.
5. Other Employment Experience: Factories may offer opportunities for in-service/on the job training with formal apprenticeship positions and also developmental training, which may help you to land your first entry-level job. Being a complete newbie, you may wonder what to add to the experience section of your resume if you have not worked in a factory before. Any working experience gained whether temporary, vocation, or seasonal regardless of whether it relates to the job of a factory worker should be added to provide substance to your resume.
6. Skills Summary/Key Skills: Factory workers need physical and technical skills to perform their duties for sure. Remember that soft skills and interpersonal traits are just as important. Pick keywords from the job posting about required competencies and personality traits and sprinkle these into your resume document for extra credibility.
What to Highlight in a Factory Worker Resume
There are many Factory Worker jobs available, but just as many candidates applying for them. Before you submit your resume to these jobs, you want to ensure it’s presenting you in the strongest possible manner. Not sure where to start? In this section, we have unpacked the most important elements to highlight in your Factory Worker Resume.
The first aspect to mention is the nature of the factory, facility, or plant you are working at. These are categorized into discrete product manufacturing or continuous product manufacturing.
- Discrete Manufacturing: These facilities make final consumer goods or sub-assemblies that is then manufactured into final products elsewhere. Parts and component manufacturing also fall into this category.
- Continuous Manufacturing: Plants producing raw materials or extracting minerals and elements and making a specific compound from it, are called continuous manufacturers. Examples include chemicals, refined oils, pulp, and paper or mineral refineries. These facilities would use heat or power to transform raw materials into finished products.
Secondly, you need to specify the nature of your job. In some cases, Factory workers are only responsible for carrying and transporting materials, machinery, and tools to designated areas. Alternatively, as a factory worker, you could be tasked with a combination of duties that could include maintenance, safety, and sanitation. The best way to highlight the purpose or scope of your job is to break it down into the main job areas of a Factory Worker
- Moving Materials, Machines, and Tools: To elaborate on your duties you could explain the type of materials, machinery or tools that you carry around all day and how you compute the quantities and volumes required by the various production stations.
- Maintenance, Sanitation, and Repairs: Preventing breakdowns, fixing equipment and ensuring appropriate ‘’housekeeping’’ are crucial activities in the factory to ensure uninterrupted production and the safety of workers.
- Purchasing and Store Supplies: If procurement and supplies are in your list of duties, mention the supplies you are responsible for acquiring like raw materials, cleaning products, fuel or safety kits.
- Operating Machinery: Machinists and operators are factory workers that specialize in running machinery and equipment in the facility. Here you could provide further details regarding the particular machines you are comfortable in operating such as CNC’s Lathes or Milling equipment.
Next, comes your physical attributes. Factory jobs are physically demanding and requiring workers to stand or sit for hours on end, frequently bending or twisting. A strong core is essential, and so is excellent vision, hand-eye, and multi-limb coordination. You could also mention the fact that you have a clear medical record and whether you can lift or move heavy objects repeatedly.
Safety and Standards are pertinent to any Factory Worker’s job due to industry regulations and compliance requirements. Mention the fact that you are familiar with ISO standards, FDA regulations for medical/pharmaceutical/healthcare facilities, or GMP protocols if you are working in manufacturing/processing environments.
Finally, provide a bit more information on the working conditions you are comfortable with. Some factory workers are involved in shift work, which could be anything from 6 hours to 12 hours in duration. If you are happy to work night shifts, accumulated a lot of overtime, or are available to work during weekends and holidays, be sure to add this as well. Often wearing cumbersome and uncomfortable gear like hazmat suits, masks or headsets are necessary for sterile cleanroom, fume laded or noisy environments, and not everybody is cut out for that. If you are used to very hot climates (boiler rooms) or freezing temperatures (cold storage) that could be an added competency to mention.
Factory Worker Resume Objectives & Examples
Hiring in factories is usually done by the Plant/Factory/Facilities Manager or the Head of Operations. They are extremely busy with very little time to read through resumes. An impact statement, such as a Factory Worker career summary comes in handy to make your application stand out from the rest.
The purpose of a career summary is to highlight your areas of expertise, showcase most prominent physical and technical attributes, and describe relevant industry experience.
Before writing your career summary, re-read the factory worker job description again and pick the keywords that stand out. Then add these to your summary, and make use of industry-specific adjectives to show the relevance of your candidacy in comparison to the vacancy at hand.
Example Resume Objectives:
Resume Objective 1
Diligent, detail-orientated, and highly technical factory professional with five years of experience in the continuous manufacturing of consumer products. Responsible for carrying and moving heavy objects and machinery to designated production stations during 12-hour shifts. Bilingual in English and Spanish and holds a Red Seal Safety certification for the lean manufacturing environment.
Resume Objective 2
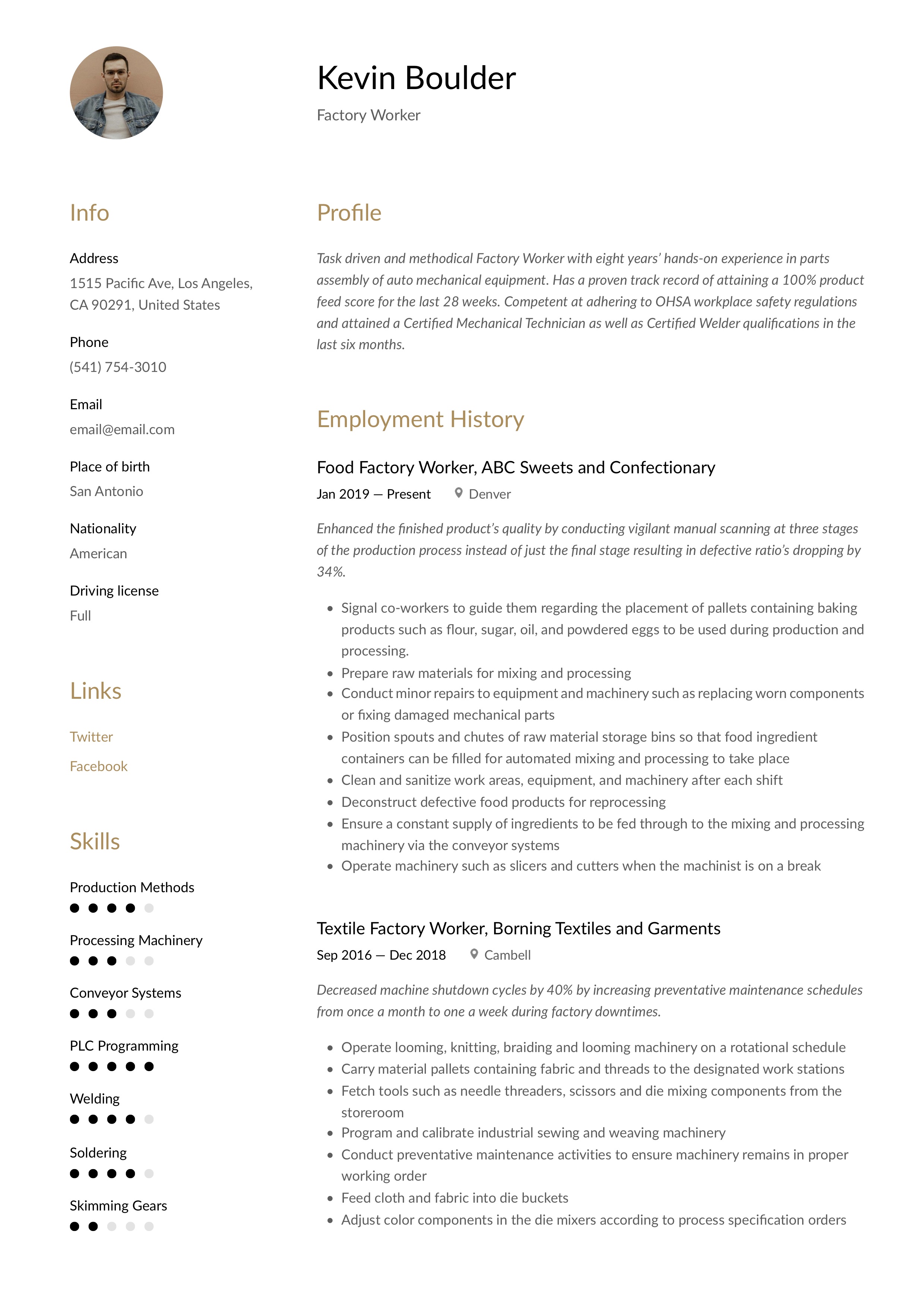
Task-driven and methodical Factory Worker with eight years’ hands-on experience in parts assembly of auto mechanical equipment. Has a proven track record of attaining a 100% product feed score for the last 28 weeks. Competent at adhering to OHSA workplace safety regulations and attained a Certified Mechanical Technician as well as Certified Welder qualifications in the last six months.
Resume Objective 3
Safety-conscious and detail orientated Factory worker with five years of experience in plastic injection molding and extrusion manufacturing processes in highly regulated environments such as medical devices and pharmaceuticals. Achieved a 99,7% accuracy rating in the last 12 months and also adept at utilizing precision cutting and PLC machinery. Currently pursuing an advanced course in Micro-Vue.
Factory Worker Job Descriptions and Responsibilities
A Factory Manager or Plant Director would expect to see certain proven duties and skill sets within a Factory Worker’s resume, depending on the type of role they fulfill at the facility or plant that they work in. To help you out we sampled job descriptions for factory workers from proven resume's below:
Examples
A Factory Worker in a Food Manufacturing Facility may:
- Signal co-workers to guide them regarding the placement of pallets containing baking products such as flour, sugar, oil, and powdered eggs to be used during production and processing.
- Prepare raw materials for mixing and processing.
- Conduct minor repairs to equipment and machinery such as replacing worn components or fixing damaged mechanical parts.
- Position spouts and chutes of raw material storage bins so that food ingredient containers can be filled for automated mixing and processing to take place.
- Clean and sanitize work areas, equipment, and machinery after each shift.
- Deconstruct defective food products for reprocessing.
- Ensure a constant supply of ingredients to be fed through to the mixing and processing machinery via the conveyor systems.
- Operate machinery such as slicers and cutters when the machinist is on a break.
A Factory Worker in a Chemical Processing Plant may
- Monitor pumps, valves, and gages to regulate the flow of liquids and air.
- Mark and tag identification on parts of the boilers and steamers to indicate the ones requiring maintenance or replacement.
- Dump materials such as organic chemicals and raw materials into machine hoppers before mixing and processing take place.
- Mix raw materials according to specified procedures or formulas before extrusion and extraction are to begin.
- Record information of products tested, meter readings on machinery, and dates and times of processing activities.
- Review charts and gauge readings and compare them with standard safety numerical values to determine that they are operating in the designated safety ranges according to OHSA.
- Measure and grade products coming out of the feeding batches in comparison to standard specifications and quality standards.
A Factory Worker in a Textile Facility may:
- Operate looming, knitting, braiding and looming machinery on a rotational schedule.
- Carry material pallets containing fabric and threads to the designated work stations.
- Fetch tools such as needle threaders, scissors and die mixing components from the storeroom.
- Program and calibrate industrial sewing and weaving machinery.
- Conduct preventative maintenance activities to ensure machinery remains in proper working order.
- Feed cloth and fabric into die buckets.
- Adjust color components in the die mixers according to process specification orders.
- Feed fabric into sewing machines and sew garments according to predetermined production specification.
- Conduct finishing duties such as cutting off loss threads, operating iron presses and affix buttons and hooks.
- Select and tag finished garments and load them onto conveyor belts.
Highlight Your Accomplishments
Writing an accomplishment section is often difficult for candidates performing manual labor or repetitive duties in a factory environment. Think about it, you are often tasked with the same activities day in and day out, have limited scope for implementing new ideas due to the job level you are on, and limited scope for ‘’ making more money for the company like your colleagues in sales and marketing.
Let's make it a bit easier then. Your goal is to think about what sets you apart, what you are most proud of, or what you accomplished in your previous roles, that saved time, ensured predetermined product outcome deadlines were adhered to, minimum downtime due to machine breakage or zero incidents due to safety issues occurred.
Now that you have written down your list of accomplishments, add a punch by incorporating numerical values such as volumes, frequencies, time frames, and percentages to each statement. This is called quantification.
Still battling a bit? Try to answer questions such as “How much?” “How often?” or “How many?” “What, When and Where”?
For instance:
- How many products do you assemble daily?
- How many safety incidents occurred in the last 12 months?
- What was the average time per product processing from mixing raw materials to loading completed product onto the conveyors?
- What is your safety incident score?
- What is the machinery breakdown cycle?
Have a look at the examples below to get you started:
- Enhanced the finished product’s quality by conducting vigilant manual scanning at three stages of the production process instead of just the final stage resulting in defective ratio’s dropping by 34%
- Decreased machine shutdown cycles by 40% by increasing preventative maintenance schedules from once a month to one a week during factory downtimes.
- Attained a 100% safety score with no incidents occurring even during peak productions times for the last six months.
- Part of the line achieving a hundred percent of quality standards with no products being flagged for defects by the quality control department and still exceeding production targets by 130%.
- Holds a 100% attendance record, coupled with a 90% quality score and a zero incident safety rating, thereby attaining Factory Worker of the Year for all ten plants in the region.
Factory Worker Education Section & Examples
The education section of your resume should still receive attention even if you do not have post-school qualifications. Factory Workers nowadays have access to multiple development training and skill improvement initiatives. Apart from your High School Diploma, you should mention inhouse-training, apprenticeship, short courses and online diplomas completed relevant to your job. If you have completed industry certifications or obtained regulatory licenses, these should be added as well. Don’t forget to include current training and education that you are in the process of pursuing.
The format for listing education and training should be kept simple and concise. In short, indicate What, Where and When: name of your qualification, institution, and date of completion.
Examples:
2018 ISA Certified Automation Professional (CAP) The International Society of Automation, Triangle Park, NC
2017 Certified Production Technician (CPT), Manufacturing Skill Standards Council, Alexandria, VA
2016 National Career Readiness Certificate, American Testing College (ACT), Iowa City, IA
2015 GED Diploma, West Side High School, Charlotte, NC
The Factory Worker Skills List
Factory workers require specific technical skills, but employers also look for other skills, such as physical traits and personal skills. Instead of listing a long array of bulleted points, use a skills matrix for each skills category (Technical, Physical, and Personal). To add a bit of flair, link an action verb to every attribute mentioned.
Technical Skills Examples
| Production & Processing | Executing technical adeptness of raw materials composition, production processes, quality control, costs, to maximize effective production and manufacturing of goods. |
| Machinery | Operating and calibrating electrical, mechanical & pneumatic machinery and equipment. |
| Maintenance | Repairing and replacing welding, soldering and brazing equipment. |
| Numerical Adeptness | Programming and coding basic tasks on computerized machines and hand-held devices. |
| Tools | Identifying and selecting most appropriate tools for example hammers, screwdrivers appropriate for the task at hand. |
| Design | Utilizing techniques, tools, and principles of products to review involved plans, blueprints, drawings, and models. |
| Quality | Conducting quality control analysis, testing, and inspections of components, products, and machinery to ensure performance and process quality standards. |
| Sanitation | Cleaning, washing, and sanitizing work surfaces, facility floors, and machinery. |
| Safety | Monitoring gauges, dials, and indicators to ensure that machinery is working properly. |
Physical Skills Examples
| Static & Trunk Strength | Exerting maximum muscle force to push, pull, lift and carry objects to designated locations. |
| Multi-limb Coordination | Climbing, twisting and bending to perform activities related to maintaining and fixing equipment. Displaying excellent flexibility and resistance to perform physically taxing tasks requiring the use of arms and legs simultaneously. |
| Concentration | Focussing on repetitive tasks for lengthy periods without disruption in concentration. |
| Physical Stamina | Standing in on place for long periods. Lifting heavy objects maintaining dexterity for hours on end. |
| 20/20 Vision | Scanning numbers and values on gauges and valves at close range and accurate interpreting figures on display boards located 20 feet away. |
| Dexterity | Moving hands and arms speedily for grasping, manipulating or assembling objects. Coordinating precise finger movements needed to push buttons and pull levers at exactly the right time to execute production processes. |
| Perceptual Speed | Comparing differences and similarities among sets of objects, patterns, numbers, and letters by quickly recalling specified ranges and scores ensuring safety standards are maintained. |
| Nimble | Instantly adjusting the controls of equipment and tools to achieve the exact placement of machine or vehicle location. |
Soft Skills Matrix
| Stress Tolerance | Handling adverse occurrences in a calm and focused manner by factory protocols |
| Teamwork | Working effectively with peers, supervisors, and managers to ensure that production targets are met and that operations run smoothly. |
| Dedicated | Maintaining high levels of perseverance and resilience to finish allocated tasks. |
| Detail Orientated | Paying attention to small details when inspecting products improving quality standards. |
| Listening | Following instructions from line supervisors to the letter and making sure all duties are performed in accordance with directions given by superiors. |
| Methodical | Following directions from supervisors at all times to ensure that set processes on the production line is executed as per the required manufacturing stages. |
| Organized | Arranging objects and prioritizing tasks in particular order batches according to a specific set of rules. |
Qualifications and Certifications associated with Factory Workers
| OSHA Certification | GED | High School Diploma |
| Fluid Power Technician | Manufacturing Technician (MT1) | Precision Sheet Metal Operator (PSMO) Certification |
| CCT – Calibration Technician Certification | Supply Chain Management (SCM) Certificate | CQT – QualityTechnician Certification |
| Hazardous Materials Transportation Training (HAZMAT) | Certified Welder (CW) | National Career Readiness Certificate |
Industries using Factory Workers:
- Construction
- Mining
- Oil, Gas & Exploration
- Medical Device
- Life Sciences
- Food Manufacturing
- Consumer Goods
- Aviation
- Aerospace
- Shipping
- Metals & Steel Production
- Plastics
- Packaging & Distribution
- Agriculture
- Electronic Components
- Power Plants
- Specialty Chemicals
- Pharmaceutical
- Industrial Engineering
Professional Information on Factory Workers
Sectors: Various
Career Type: Production, Fabrication, Processing, Manufacturing, Engineering, Industrial, Assembling, Extracting
Person type: Worker, Fabricator, Assembler, Checker, Handler, Sorter, Mover, Operator
Education levels: From High School Diploma to Post School Education
Salary indication: Factory workers get paid by the hour (*Payscale)
Low: $ 9.74 p/h, Median: $ 13.45 p/h High: $ 19.85 p/h
Labor market: Varies depending on Job Type
Assemblers & Fabricators: Decline of 16% from 2016 – 2026
Food & Tobacco Workers: Increase of 2% from 2016 – 2026
Metal & Plastics Workers: Decline of 9% from 2016 – 2026
Welders, Cutters, Brazers, and Solderers: Increase of 6% from 2016 – 2026
Organizations: Plants, Factories, Production Facilities, Manufacturing Operations
Download Factory Worker Resume Examples

Factory Worker – Resume (0).PDF

Factory Worker – Resume (1).PDF
Factory Worker – Resume (2).PDF

Factory Worker – Resume (3).PDF
Factory Worker – Resume (4).PDF

Factory Worker – Resume (5).PDF
Factory Worker – Resume (6).PDF

Factory Worker – Resume (7).PDF
Factory Worker – Resume (8).PDF
Factory Worker – Resume (9).PDF

Factory Worker – Resume (10).PDF